Type Conversion
Type conversion is the process of converting one data type to another. In C, there are two types of type conversion:
- Implicit Type Conversion
- Explicit Type Conversion(a.k.a Type Casting)
and there are two rules of type conversion:
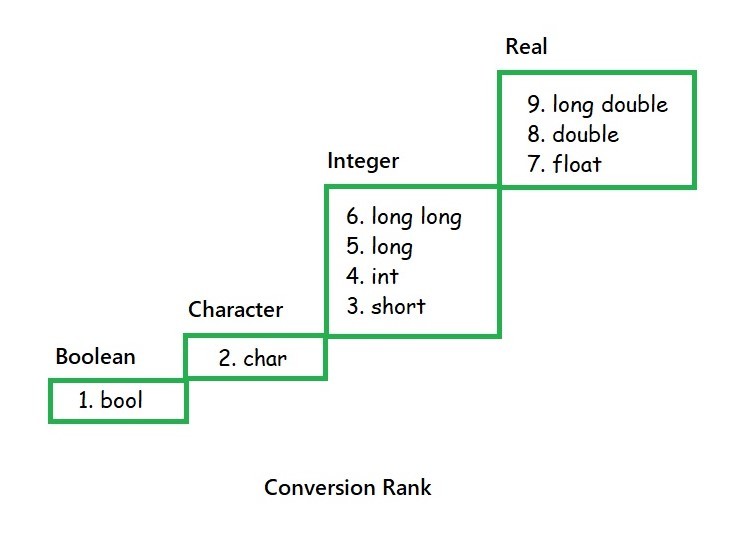
- Widening Conversion: When a data type of lower rank is converted to a data type of higher rank. Applicable in expressions.
- Narrowing Conversion: When a data type of higher rank is converted to a data type of lower rank. Can be applicable in both expressions and assignments. Generally applicable in assignments.
Implicit Type Conversion
Implicit type conversion is done automatically by the compiler. It is also known as coercion. In this type of conversion, the compiler automatically converts one data type to another without any user intervention. This is done when the data type of the expression is automatically converted to a “higher” data type.
signed will be converted into unsigned
if one operand has an unsigned type whose conversion rank is at least as high as that of the other operand’s type, then the other operand is converted to the type of the operand with the higher rank.
Explicit Type Conversion
int a;
a = 2 + (int) 3.5;
// 2 + 3;
// 5;
int a;
a = 2 + (int) 3.5;
// 2.0 + 3;
// now compiler will do implicit coversion
// 2.0 + 3.0;
// 5.0;